“z+ Ec 98 A8 Eb 9d Bc Ec 9d B8 Ed 8c Ec 9b 8c Eb B3 Bc+cddc7 Com+ E2 96 B3 Eb B3 B4 Eb 84 88 Ec 8a A4 Eb B2 88 Ed 98 B8+b77 E2 96 B3 Ea B3 A0 Ec 9d 98 Ec 82 Air Conditioning Ea B5 Air Conditioning Unit E2 9e 80 Ea B3 84 Ec 96 91 Eb B0 94 Ec B9 B4 Eb 9d Bc F0 9f A5 Be Ec B6 95 Ea B5 Ac Eb Air Conditioning Unit B4 Eb A3 8c Ed 94 Bd E3 83 87 Ec 9d B8 Ec B2 9c+1xbet C5 93 Ec 98 A8 Eb 9d Bc Ec 9d B8 Ed 8c Ec 9b 8c Eb B3 Bc Ec B6 94 Ec B2 9c+kromesky Jobs In Egypt 2024
January 16, 2023Топ-3 White Label Платформ Для Форекс Брокеров
January 19, 2023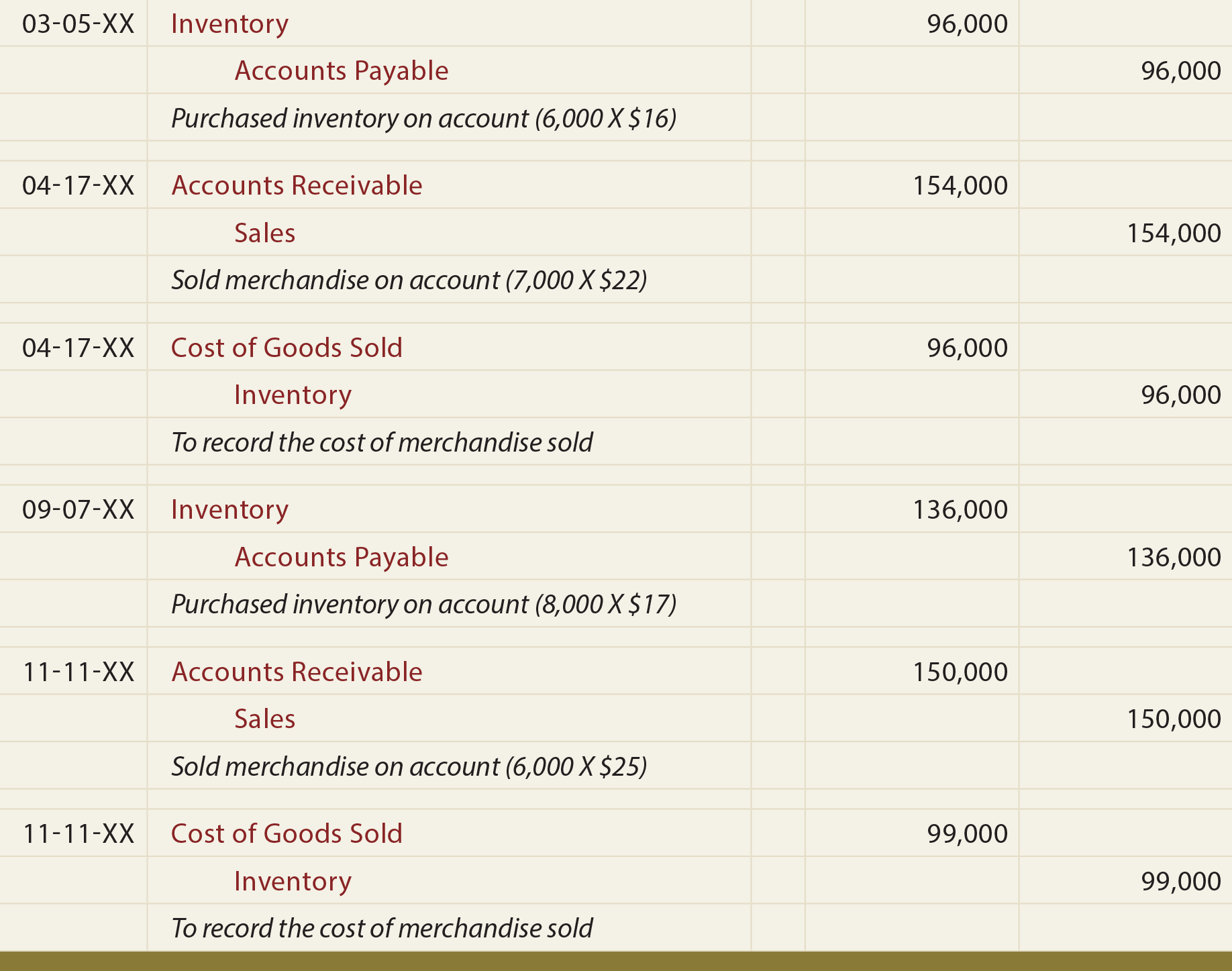
When the credit customer returns to pay off his account, cash is collected however. A cash book is set up as a subsidiary to the general ledger in which all cash transactions made during an accounting period are recorded in chronological order. The primary goal of a cash book is to manage cash efficiently, making it easy to determine cash balances at any point in time, allowing managers and company accountants to budget their cash effectively.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Credit – What went out of the business The obligation of the customer to pay and therefore the assets of the business have been reduced.
How to manage a cash receipts journal?
Read on as we take a closer look at what a cash receipts journal is, the different types, and the pros and cons. In practice the entry to the accounts receivable would be a two stage process. The amount would be posted to the sales ledger, to the individual account of the customer, and then the control totals in the sales ledger would be posted to the accounts receivable control account. In this case the debit entry to the cash account represents the cash collected from customers for the period, which increases the asset of cash. It is important to understand that if any cash is received, even if it relates only to a part of a larger transaction, then the entire transaction is entered into the cash receipts journal. To log these transactions in a cash receipts journal, each of these transactions is entered sequentially into the journal in the appropriate column.
What Happens If You Lose Track of Cash Receipts?
GAAP attempts to standardize and regulate the definitions, assumptions, and methods used in accounting. There are a number of principles, but some of the most notable include the revenue recognitionprinciple, matching principle, materiality principle, and consistency principle. A cash receipts journal is used to record all cash receipts of the business. Along with each sale of goods, there is a related cost of goods entry that must be booked to record the inventory being sold. When the inventory is delivered to the customer, it is taken off the books for the cost originally paid as a credit to inventory. The Cost of Goods Sold account, and expense account, is debited for the same cost as the inventory was recorded at, as shown below.
What is recorded in the sales journal?
When recording cash receipts, increase, or debit, your cash balance. Recording cash receipts offsets the accounts receivable balance from the sale. There are numerous reasons why a business might record transactions using a cash book instead of a cash account. Mistakes can be detected easily through verification, and entries are kept up to date, as the balance is verified daily.
Record the cash receipt transaction

A copy of this receipt is given to the customers and another copy is retained for accounting purposes of a business. It has several uses including records for cash sales, balancing accounts receivable and payable, and reconciliation of accounts. The cash receipts journal can be subdivided into different sections as well. For example, many companies want to know and evaluate the amount of cash they collected from sales, credit customers, and other sources. The balance in the cash receipts journal is regularly summarized into an aggregate amount and posted to the general ledger. At a minimum, the transactions in the journal should be posted to the general ledger at the end of each reporting period, though posting may be conducted on a daily basis.
- Cost of sales is also known as the cost of goods sold, and the two terms are used interchangeably.
- There are several types of cash books that entities can use, whether they’re businesses or individuals.
- So a typical sales journal entry debits the accounts receivable account for the sale price and credits revenue account for the sales price.
- This way an accountant or bookkeeper can analyze the amount of cash collected and recorded during a period separate from all other journal entries in the general journal.
The single-column cash book is the easiest type of cash book to use. This type is commonly used by individuals who want to keep track of their own money and finances. To use the cash receipt journal entry single-column version of the cash book, transactions are noted in one column. A cash receipt is documented record of the account of cash received in the cash sale transaction.
This way, the business owners are always on top of bills that are paid and ones that are still outstanding. The physical or electronic owner’s copy of the cash receipt is called a source document in the accounting for cash receipts. Source documents are the proof that a sale was actually made and payment received. It should be kept for income tax reporting purposes and to support your financial statements. If you use bookkeeping or accounting software, you can conveniently store one copy with the sale.
Your cash receipts journal should have a chronological record of your cash transactions. Using your sales receipts, record each cash transaction in your cash receipts journal. The cash receipts journal is used to record all transactions that result in the receipt of cash. Again, in the general ledger accounts, the post reference “CR-8” is recorded to indicate that these entries came from page 8 of the cash receipts journal.
The use of the journal saves time, avoids cluttering the general ledger with detail, and allows for segregation of duties. Additionally in some businesses, the cash receipts journal is combined with the cash disbursements journal and is referred to as the cash book. The first three columns in the diagram are the date, transaction description (Desc.), and ledger folio reference (LF). The single column referred to in the name of this cash ledger book is the monetary amount of the cash receipt (Cash) highlighted in gray.